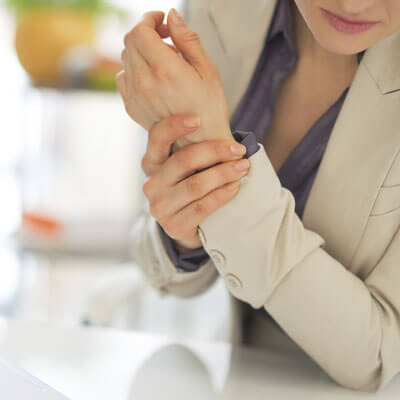
You may have heard the term inflammation being used to describe the swelling that happens when you get injured. This type of swelling is considered acute (short-lived) and is a response from your body to send the appropriate cells to heal the affected tissue. Immune cells will release various substances such as hormones bradykinin and histamine. They cause the small blood vessels to become wider (dilate), letting more blood to get to the injury. For this reason, inflamed areas turn red and feel hot. Both of these hormones also irritate nerves and cause pain signals to be sent to the brain.
Different areas of the body will swell at different rates when they are injured. Areas that are highly vascularized (supplied with more blood vessels than others) like the ligaments in your ankles or the discs in your spine, will have more inflammation happen as they heal. Typically, acute inflammation can last 6 – 10 days and the body will naturally reduce it once the injury is healed.
Chronic (long-term/persistent) inflammation can occur due to many reasons. Sometimes it is a response to systemic disease and other times it can be a response to your body reacting to a “perceived” injury – one that may not lead to a damaged tissue but perhaps mimics the presentation of one due to poor mechanics.
Whatever the reason may be for chronic inflammation, it is a largely concerning problem because it affects different areas of the body. When a local area gets inflamed due to injury for a short term, the inflammatory cells are limited to that region. With chronic inflammation, the inflammatory cells can stay elevated in your blood stream and affect different areas of the body. Research shows that chronic inflammation can contribute to heart disease, diabetes, arthritis or even cancer.
The good news is that there are a lot of natural ways to at least reduce chronic inflammation (even if it cannot be completely treated due to another health issue). Things like eliminating pro-inflammatory foods from your diet, taking the right supplements, breathing techniques and meditation/exercise have shown to effectively help with reducing levels of chronic inflammation. Next time, we will elaborate on a few of these suggestions that you can start at home to manage chronic inflammation.
CONTACT US